Since the reform and opening up, China has been called the “beast of the Far East†due to the rise of the manufacturing industry. This metaphor shows the sheer size of China's manufacturing and also implies the roughness of Chinese manufacturing.
Strong investment impulses, leaving behind the income of residents, and staying in the competitive thinking of cost-leading strategies have created two major problems in China's manufacturing industry: large-scale overcapacity and industrial hollowing.
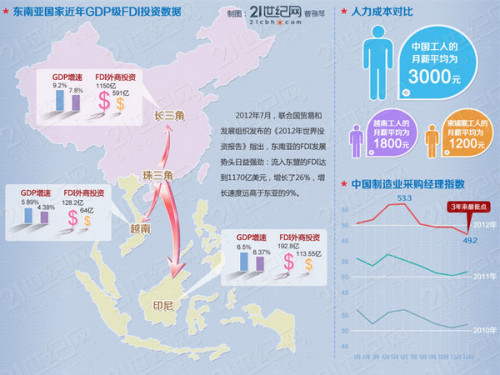
Who initiated the industry to move west, what is the original driving force, who is the initiator, China’s demographic dividend is gradually decreasing, and rising labor costs are an inevitable trend. When the “Beast of the Far East†began to be threatened by the relocation of high-end manufacturing industries in Europe and the United States and Vietnam, Indonesia and other emerging countries, we must not only think about how to rely on transformation and upgrading to solve the predicament.
Made in China, where is the breakfast tomorrow?
The problems encountered by Chinese manufacturing today are also problems that Japanese manufacturing and Korean manufacturing encountered yesterday. For example, until 1970, South Korea mainly exported textiles, but today South Korea mainly exports automobiles, chips and mobile phones. Both Japan and South Korea have successfully overcome the difficulties facing Chinese manufacturing today.
At present, there are numerous cases in which the Chinese economy is faced with a “bleeding transformationâ€: household appliances retail industry, Gome, and Suning have created billions of dollars in debt to build e-commerce by replacing real estate and stocks. Qingdao Haier Group has acquired Fisher & Paykel, the New Zealand-based household appliance giant Fisher & Paykel, as a global player.
In the textile consumer industry, Li Ning is under pressure from raw materials, labor, and inventory, and the CEO will be able to finish classes and close the stores to save themselves. Heavy industry equipment and machinery industry, 4 trillion investment sequelae have not dissipated, Sany Heavy Industry has ushered in a slowdown in layoffs, China Ocean Shipping battle cycle, and Baosteel, Anshan Iron and Steel and other steel companies, there are selective acquisitions and mergers, reduce steel volume To seek the reverse growth under the 2 trillion economic stimulus...
The overall situation in China's manufacturing industry is not optimistic. The old topic of “transition†has never been as realistic and urgent as today. The above companies are all "leaders" in the history of Chinese manufacturing. Textiles, shipbuilding, heavy machinery, photovoltaics, and retail consumer sectors are the hardest-hit areas for industrial hollowing.
Shi Wei of the National Development and Reform Commission's Institute of Economic System and Management believes that the upgrading of China's manufacturing industry faces a major institutional problem. In the future, if China's manufacturing industry wants to get out of stagnation, it must eliminate the control of power over resources and markets.
He believes that from the current situation in China, especially the transition of small and medium-sized enterprises, within 3 to 5 years, China's manufacturing and processing industries have the most breakthroughs in mechanical and food processing industries.
“These two industries are: First, large enterprises, intensive and number-distributive industries, backward industrial grades, and disconnected production capacity and technology supply; second, the alternative investment and financing channels have not been opened. These two industry breakthroughs can drive China's manufacturing industry. The overall follow-up has a very good demonstration effect on technological transformation, investment, and upgrading of enterprises. More importantly, the improvement of these two industries is enough to significantly increase China's industrial export initiative."
Shi Wei believes that completely abandoning the special treatment of state-owned enterprises and encouraging private enterprises to take the initiative to innovate and introduce technology is the key to eliminating the simple "quantity-for-market" of the machinery industry.
At present, the reality we must face squarely is that more countries are not able to leapfrog the “middle income trap†when faced with transformation and upgrading. Some countries in Latin America and Southeast Asia are typical representatives. Among the economies that have successfully crossed the "middle income trap", Japan and South Korea alone have larger scales. Today's China is even larger than Japan and South Korea.
Surrogate, pregnant without first-class "Made in China"
China created and sold the market, but did not switch back to advanced technology. This phenomenon is prominent in the "multinational" industries such as beverages, beer, detergents, cosmetics, and high-tech industries such as computers and mobile communications.
Since the 1990s, with the development of the status of China's manufacturing division of labor, multinational companies have set off an upsurge of R&D investment in China. Microsoft, Motorola, Procter & Gamble, Unilever, DuPont, Intel, Nokia, Ericsson, Panasonic, Fujitsu and other Fortune 500 multinational companies have established R&D centers in China or announced large-scale R&D programs.
However, the deterioration of international trade conditions and the lack of core technologies in technology-intensive industries have made China's manufacturing industries “backwardsâ€.
A former Intel technical director told the 21st Century Network: "Intel's R & D centers in China are wholly owned. Frankly speaking, multinational companies are mostly like this. If they have the so-called technical cooperation with China, they are basically forced. â€
At present, the level of technology transfer by multinational corporations is still low. Multinational corporations use China's total labor force and cost advantages, and are mainly engaged in the assembly and processing of final products in China, while key components still rely heavily on imports.
In the summer of 2010, Foxconn jumped continuously and marked the end of the "low-cost era" of Chinese manufacturing, and it was also the beginning of various "bad-mouthed" Chinese manufacturing industries. Let us wake up. Yes, surrogacy, we cannot always produce first-rate Chinese manufacturing.
Former Intel technology executives further explained this principle to 21st Century Network: “Actually, it is understandable. The multinational company’s R&D center still has to proceed from the interests of the company. From the standpoint of shareholders’ interests, it will certainly retain its core technology. ."
“The core technologies of multinational companies include advanced manufacturing processes and the corresponding application and commercialization of technologies. At present, this part of the technology is mainly realized in multinational companies in the country. “Technological problems are related to many aspects. Ordinary applications, there are professional, customized; can be civilian, but also may involve military use, so it is understandable on the home. â€
In September 2012, the China Enterprise Confederation released the "hollowing out" phenomenon for the first warning manufacturing industry of the "2012 China Top 500 Development Report." The profit of the top 500 banks far exceeds that of the manufacturing industry, and the "gap" between the manufacturing and commercial banks is continuing to expand.
We should see multinational corporations in China R & D institutions, to bring learning opportunities for local talent. “The R&D system and process of multinational corporations will greatly help improve the quality of local Chinese developers.â€
Pioneers say: The rise of Huawei
However, there are no shortage of pioneers in the transformation and upgrading. The rise of Huawei can be regarded as a model for the success of Chinese manufacturing.
In an environment where the global communications equipment industry is generally declining, Huawei's sales revenue in the second quarter of this year reached 102.7 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 5.1%.
This is the first time that Huawei has surpassed Ericsson in terms of revenue, and has been ranked among the top three in the world in terms of revenue: Operator network business, enterprise market ICT solution business and consumer business have all performed well. Among them, mobile phone shipments exceeded 10 million in the first half of the year. In the first half of the year, Huawei Terminal China achieved sales of more than 10.9 billion yuan, and completed more than half of the annual tasks. Mobile phone sales reached 10 billion yuan, an increase of 193 percent year-on-year.
The "big brother" Ericsson net sales rose by only 1% in the second quarter, net income fell 63%; the world's third Alcatel-Lucent has previously issued performance warnings, is expected to second quarter operating losses of more than 40 million euros, can not reach 2012 The profit target; Nokia Siemens second-quarter sales fell 8% year-on-year, and plans to layoff 17,000 people by the end of 2013.
Huawei’s status today benefits from the emphasis on R&D and timely transformation. And most Chinese manufacturing industries are too “coveted†for the economic transformation system dividend, and do not pay attention to different science and technology research and development. As early as in 1989, Huawei set up its first overseas R&D institution in Bangalore, India. Today, Huawei has set up 23 research institutes overseas and established 34 joint innovation centers with mainstream operators around the world to avoid the development of hollowing out.
Lu Zheng, head of the Institute of Industrial Economics of the former Academy of Social Sciences, pointed out: "Technology is a dynamic concept. Mastering a certain technology does not mean having the ability to develop technology. Today's new technology is not equal to tomorrow's new technology."
"From the perspective of residual claims for technology, the technologies owned by multinational corporations and the technologies owned by local companies have a considerable impact on the national welfare of a country. If we do not consider the issue of residual claims, we will look at the market from a static point of view. For technology, multinational companies have undoubtedly brought new technologies, but if technological innovation is considered, there will be a logical disconnect between stock technology and technological innovation."
Take Apple's mobile phone as an example, China is Apple's second largest market in the world, and hundreds of millions of China's "fruit powder" have become obsessed with Apple's obsession and its contribution to its performance. Foxconn as the representative of Greater China enterprises is to support Apple's global industrial empire is an important part, but the famous foundry giant Foxconn, only benefit from the iPhone value chain 1.8%.
Lu Zheng pointed out that Chinese companies prefer the introduction of technology and then the “total cost leadership†strategy. They often have insufficient understanding of the differentiation strategy and agglomeration wars and lack of enthusiasm for technological innovation.
At present, troubled entrepreneurs are finally beginning to realize the importance of independent technological innovation. However, under the influence of multiple factors such as the economic downturn, the long period of R&D investment, and the ineffectiveness of domestic intellectual property protection, more Huawei will be born. Not a day's work.
Why can't I stop overcapacity?
Excess has become the prevailing status in China's manufacturing industry.
The overcapacity is the problem of "quantity" of China's manufacturing industry. We still have a great deal of initiative in solving this problem. But the problem of hollowing out the manufacturing industry caused by the lack of core technologies is even more complicated.
Data show that 70% of China's textile machinery, 75% of high-end machine tools rely on imports, 75% high-speed offset press, 85% integrated circuit chip manufacturing equipment, almost 100% of optical fiber manufacturing equipment, 40% of large petrochemical equipment, 70% of the Automobile manufacturing key equipment and advanced intensive agricultural equipment still rely on imports. There are less than 20% of products with independent brands. It is also these industries that have fallen into difficulties.
Nowadays, industries with serious hollowing out of these industries are also industries that have been trapped in the economic recession.
In general, the industries with the most severe overcapacity at present include seven industries: ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals, petrochemical coking, chemical raw materials, non-metallic mineral products, chemical fibers and paper products. Most of these industries were also mentioned in 2009 by the State Council, which approved the issuance of "Several Opinions on Suppression of Overcapacity and Repeated Construction in Some Industries and Guidance of Several Opinions on the Healthy Development of Industries" (hereinafter referred to as the "Notice") issued by various departments of the State Council.
The "Notice" pointed out that "special attention needs to be paid to the fact that not only the traditional industries such as steel and cement, which have excess capacity, are still expanding blindly, but also the emerging industries such as wind power equipment and polysilicon have experienced repeated construction." The specific industries named include steel. , cement, flat glass, coal chemical, polysilicon, wind power equipment, electrolytic aluminum, shipbuilding, soybean crushing and other industries.
Analysts pointed out that most of the overcapacity industries are in the heavy industry sector and have a monopolistic nature of competition. Therefore, overcapacity is prone to occur. The most direct and obvious result of overcapacity is the drastic fall in product prices. At the same time, the inventory of finished products has increased, the industrial enterprises have been seriously underdeveloped, and the capacity utilization rate has decreased. This has led to a substantial decline in corporate profits and an increase in loss-making enterprises.
21st Century Network has previously reported on the Chinese steel industry, shipbuilding and other industries. These industries are suffering from overcapacity and severely declining profits.
Yuan Jiemin, an associate professor at Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, believes that taking GDP as the core of performance evaluation and taking into consideration the local government officials' responsibility for selection of local officials has a very large incentive for local governments to drive GDP through investment. This will also lead to overheated investment and overcapacity. .
Lin Yifu believes that the characteristics of China's economic development stage is also one of the important reasons for excess production. In developing countries, there is a large influx of investment from the social consensus on the good prospects of the industry, leading to the phenomenon of overcapacity.
One of the most common under the guidance of a cost leadership strategy is the "price war." For example, in the home appliance industry, home appliance companies were abducted twice in 10 years from the US-Soviet hegemony during the period of home appliance chain stores to the three-nation killings in the Beijing-Su-US electricity supplier field. Unfortunately, they were victims of changes in the business model.
Zhang Ruimin, chairman of Qingdao Haier’s Board of Directors, lamented: “The biggest question now is where are the road signs? We will enter an era without signposts.†China's manufacturing industry, which has “frustrated†due to the financial crisis, is now working hard to return to transition. On the orbit, where is our road sign? This is a test that is thrown under the baptism of a new round of economic cycles.
Shock Collar Charger,Dog Training Charger,E Collar Charger,Dog Shock Collar Charger
Elite-tek Electronics Ltd , https://www.aetertek.ca