The functional block diagram of the satellite system is shown in the figure below:
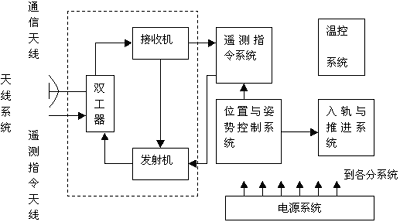
As can be seen from the above figure, the main satellite equipment includes the following seven systems.
(1) Position and attitude control system
Theoretically, the position of a geostationary satellite is stationary relative to the earth, but in fact it is not always able to maintain this relatively stationary state. This is because the earth is not a true spherical shape, which affects the relative velocity of the satellite to the earth. At the same time, when the radiation pressure of the sun and the moon changes strongly, the relative position of the satellite to the earth will also be destroyed due to the interference they generate on the satellite. These will cause the satellite to drift out of orbit, making communication impossible. Responsible for maintaining and controlling your position on the track is one of the tasks of the track control system. It is not enough to keep the satellite in the designated position in orbit, but it must also have a correct attitude in this position. Because the beam of the directional antenna on the satellite must always point to the center of the earth or the center of the coverage area. Since the directional beam is only a dozen degrees or narrower, the beam pointing is greatly affected by the attitude change of the satellite. In addition, the satellite is 36000KM away from the surface of the earth, and the attitude difference is a few centimetres, which will cause the antenna to point a thousand miles. Furthermore, the surface of the solar cell must always face the sun, all of which require satellite attitude control.
(2) Antenna system
The antenna system of the communication satellite includes a communication antenna and a telemetry command antenna. The two antennas are required to be small in size, light in weight, high in reliability, long in life, high in gain, and the beam always points to the earth, using a racemic antenna and an omnidirectional antenna respectively.
(3) Repeater system
The space transponder system is the main body of the communication satellite. It is actually a high-sensitivity broadband transceiver. Its intelligence is to forward wireless signals with minimal additional noise and distortion and the highest possible amount of amplification.
(4) Telemetry command system
The main task of the telemetry command system is to tell the satellite measurement and control station on the ground originally about the working status of the equipment on the satellite, and to faithfully receive and execute the command signal sent from the ground measurement and control station.
(5) Power supply system
The power of modern communication satellites uses both solar cells and chemical batteries. The power supply system is required to be small in size, light in weight, high in efficiency, and long in life.
(6) Temperature control system
The temperature control system can keep the temperature inside the satellite and the surface within the allowable range, otherwise it will affect the performance and life of the electronic equipment on the satellite, and even malfunction. In addition, when the temperature difference on the satellite housing or the antenna is too large, deformation often occurs, which will adversely affect the direction of the antenna and the accuracy of the sensor and the directionality of the nozzle.
(7) Orbiting and propulsion system The orbit control system of the stationary satellite is mainly composed of axial and lateral jet propulsion systems. The axial nozzle is used to control the drift of the satellite in the latitude direction, and the lateral nozzle is used to control the drift of the satellite in the longitude direction due to the change of the satellite's surrounding speed. The nozzle is composed of a small gas (a kind of gas fuel) rocket. Its ignition timing and gas duration are controlled by the control signal sent from the ground measurement and control station to the satellite.
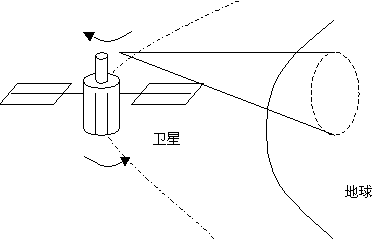
Another function of the propulsion system is to perform attitude control on the satellite using methods such as spin stability, gravity gradient stability, and magnetic stability.
The attitude control method shown in the figure is spin control. When this satellite is sent to the sky, it is rotated at a speed of 10 to 100 revolutions per minute by a rotating device in the rocket before it is separated from the rocket. The rotating satellite is like a gyro, and the axis of rotation always points in one direction, so it won't roll over at will. However, the antenna mounted on the satellite axis cannot rotate with the star, so a derotation device should be installed to make the antenna aim firmly at the earth.
Polyester Tipped Swabs,Cleanroom Polyester Swab,Sterile Polyester Tipped Applicators,Flat Rectangular Head Swab
Miraclean Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.mrccleanroom.com