When the frequency is high, the capacitor can no longer be treated as a simple lumped element, and the effects of parasitic parameters become significant. These parasitic elements include the equivalent series resistance (ESR) and the equivalent series inductance (ESL), which play a critical role in determining the performance of the capacitor at high frequencies.
The actual equivalent circuit of a capacitor includes several components: C represents the static capacitance, while Rp is the leakage resistance or insulation resistance. This resistance is typically very high, often in the GΩ range, which means that the leakage current is minimal and the capacitor performs reliably. In most practical applications, Rp can be neglected due to its large value. Additionally, there are dielectric absorption effects, represented by Cda (dielectric absorption capacitance) and Rda (dielectric absorption resistance). Dielectric absorption refers to the phenomenon where a capacitor retains some charge after being discharged, and this stored charge gradually returns over time.
Among all the parasitic parameters, ESR and ESL have the most significant impact on the high-frequency behavior of the capacitor. To simplify analysis, a series RLC model is commonly used, as shown in Figure 1(b). This model helps calculate the resonant frequency and the equivalent impedance of the capacitor.
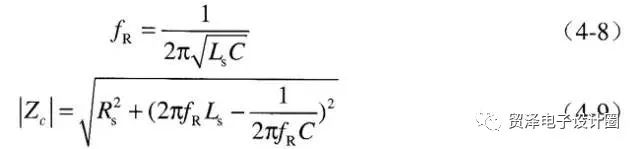
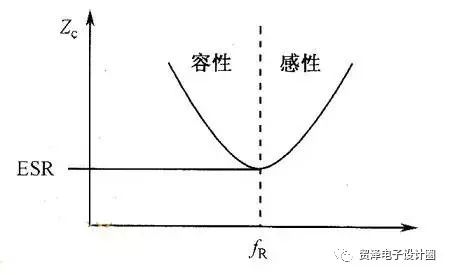
The frequency domain impedance plot of the series RLC model is illustrated in Figure 2. Below the resonant frequency, the capacitor behaves capacitively, while above it, it exhibits inductive characteristics. As a result, the decoupling effectiveness of the capacitor decreases at higher frequencies. The equivalent impedance first decreases and then increases with frequency, reaching a minimum value at the resonant frequency, which is equal to the ESR.
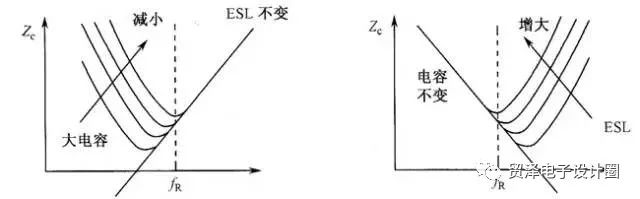
From the resonant frequency formula (4-8), it’s clear that both the capacitance value and the ESL significantly affect the resonant frequency of the capacitor, as shown in Figure 3. Since the impedance is lowest at resonance, it's ideal to select capacitors whose resonant frequency (fR) closely matches the operating frequency. In environments where the operating frequency varies widely, using a combination of a large capacitor with a low fR and a small capacitor with a high fR can help maintain effective decoupling across a broader frequency range.
Porsche Dashcam,Dash Cam With G Sensor,Dash Cam With Loop Recording
SHENZHEN ROSOTO TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. , https://www.rdtkdashcam.com